DHCPv6 as a concept is very similar to version 4. There are some key differences that we need to know. DHCPv6 supports two very different methods; Stateful and stateless configurations.
Stateful
Stateful configuration works pretty much the same as DHCPv4. The DHCP server assigns the IP address to the client. When DHCPv6 addresses are being sent from a server to a client it uses UDP destination port 546
Stateless (SLAAC)
- A-flag - if it is set to 1, this informs hosts that they can auto-generate GUA address using SLAAC. If it is set to 0 means that auto-configuration is not allowed for this segment.
- O-flag - if it is set to 1, this informs hosts that they can obtain a DNS server list and a domain name from a Stateless DHCPv6 server, but not addressing information. Typically it works in conjunction with SLAAC for auto-addressing and both the A-flag and the O-flag are set to 1.
- M-flag - if it is set to 1, this informs hosts that they can obtain a global address as well as DNS and a domain name from a Stateful DHCPv6 server. Typically this means that auto-addressing using SLAAC is not allowed on this segment and both the A-flag and the O-flag are set to 0.

2. On the router use the below configurations from the screenshot;
Configurations
Lets look at how we configure SLAAC;
1. Build a simple network similar to the below
-ipv6 unicast-routing (enables the router for IPv6 routing)
-interface gigabitethernet0/0/0 (this is the particular interface being used for the connection to the switch)
-ipv6 address (is an IPv6 address which in this instance in the address of the router)
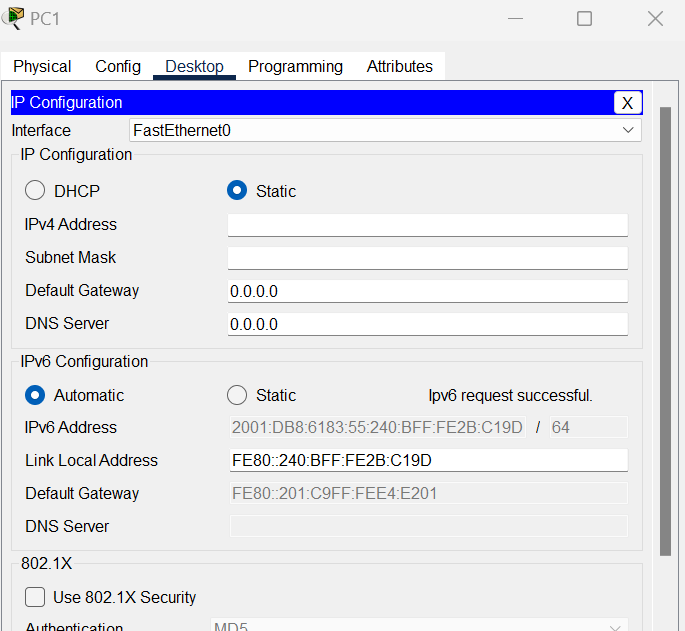
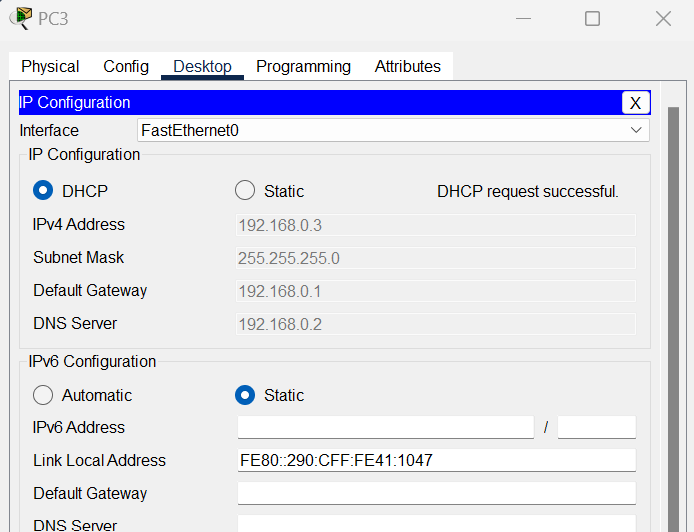
3.On each PC change the IPv6 configuration to automatic.
You will now find that the PC generates a Global Unicast Ipv6 Address on its own, with the Default Gateway address and the Link-Local Address from the Router Advertisement.
Ipv6, SLAAC and EUI
- The hexadecimal value of FFF0(16-bits) is added in the middle of the 48-bit mac address.
- The 7th bit from the start is toggled from 0 to 1.
For example:
For the MAC address FC:99:47:75:CE:E0 the steps are performed as shown in the below:
Cisco routers are configured to use the EUI-64 ID generation by default.
Here is a video showing the configuration in action;