Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a layer 2 protocol. It simply maps an IP address to a mac address.
When a PC communicates with another the arp table is updated with the command arp -a (shown below)
Why DAI?
Within a man-in the middle attack - typically arp spoofing. A rogue pc/laptop sends a spoof arp message which associates the attackers mac address with that of the router or other device on the network so that it can intercept and alter traffic. DAI on the switch compares the incoming ARP packet and entries should be matched in the DHCP snooping binding table, and any ARP access control lists. If the ARP doesn't match the switch will disregard the ARP request.
Configurations
To configure DAI and validate the source mac address against the sender's mac address within the ARP body we use this can be seen in the show ip arp inspection image that src mac address is validated;
And verify the configuration:
Access control
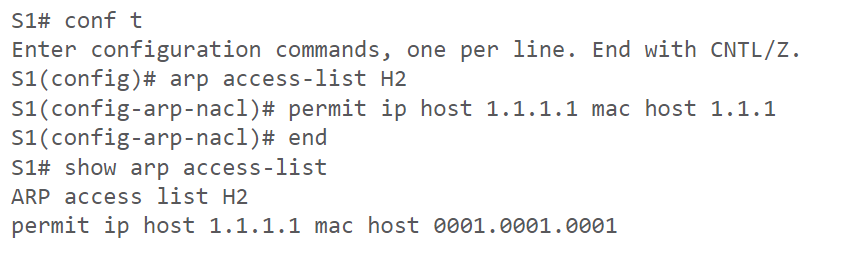
Cisco packet tracer doesn't currently support the creation of ARP access lists but essentially it is permitting the access of an IP address and MAC address through an interface just like the below






No comments:
Post a Comment